[Data Structure] 트리(Tree)
Updated:
Goal
- Tree와 Binary tree의 구조를 이해한다
- Linked list를 통해 Tree를 구현할 수 있다
Tree
- 트리는 하나 이상의 노드를 가지는 형태로 구현된다.
- root 노드는 0개 이상의 자식노드를 갖는다.
- 그 자식노드들 또한 0개 이상의 자식노드를 갖는다. 이는 반복적으로 정의 된다.
- 트리는 사이클이 존재하지 않는다.(사이클이 없는 하나의 연결 그래프)
Tree와 관련된 용어
- root node : 부모가 없는 노드로 트리는 하나의 루트 노드만을 가진다.
- leaf node(단말노드) : 자식노드가 없는 노드
- edge(간선) : 노드를 연결하는 선
- size(노드의 크기) : 자신을 포함한 모든 자손 노드의 개수
- depth(노드의 깊이) : 루트에서 어떤 노드에 도달하기 위해 거쳐야 하는 간선의 수
- level(노드의 레벨) : 트리의 특정 깊이를 가지는 노드의 개수
- degree(노드의 차수) : 하위 트리 개수 / 간선 수 = 각 노드가 지닌 가지의 수
- degree of tree(트리의 차수) : 트리의 최대 차수
Tree의 종류
Tree vs Binary Tree
- 이진 트리(Binary Tree)
- 각 노드가 최대 두개의 자식을 갖는 트리
- 모든 트리가 이진트리는 아님
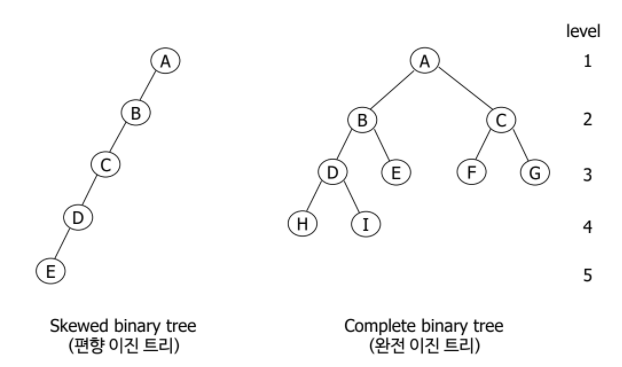
Complete Binary Tree
- 트리의 마지막 레벨을 제외하고 모든 레벨에서 노드가 꽉 차 있는 이진트리
- n개의 노드를 가지고 있는 완전 이진 트리에서의 높이 : log2(n+1)
Binary tree representation
Array representation
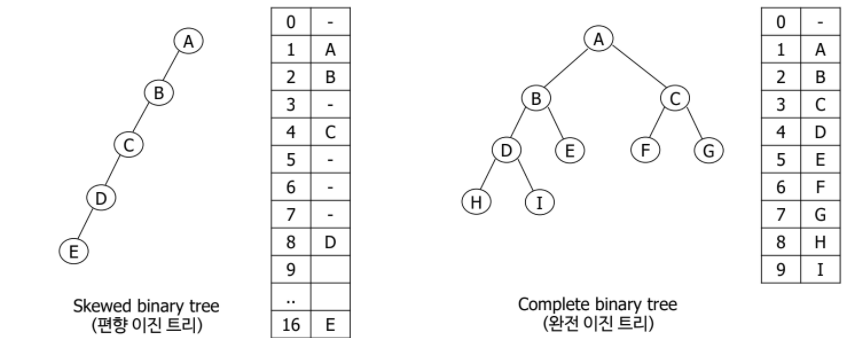
- 1차원 배열에서 k에 부모 노드를 저장하고 2k, 2k+1에 각각 left_child, right_child 노드를 저장한다.
배열을 이용한 이진 트리 저장의 문제점
- 배열에서 이용하지 않는 저장 공간이 많다
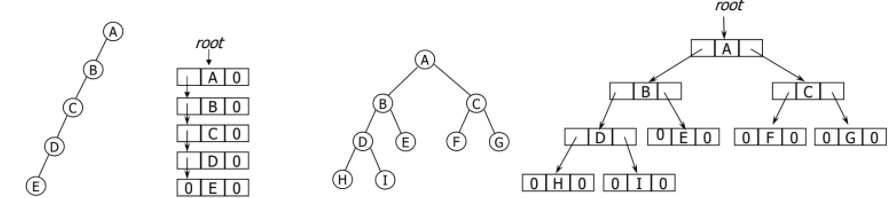
Linked list

typedef struct node * treePointer;
typedef struct node{
int data;
treePointer leftChild, rightChild;
} node;
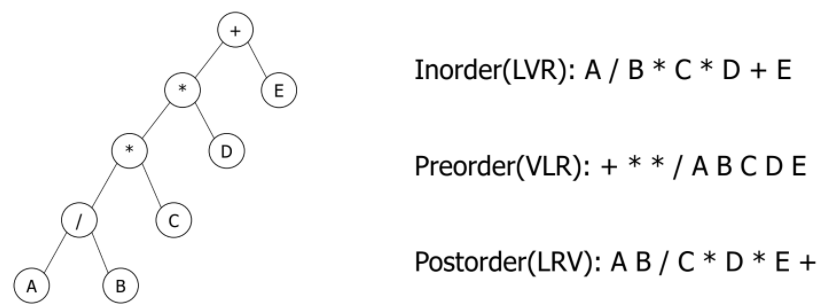
Binary tree traversal
- 트리 탐색 방법
- 가능한 탐색 방법 : LVR, LRV, VLR, VRL, RVL, RLV
- L : moving left, V : visiting the node, R: moving right
- 중위 순회(inorder) : LVR
- 전위 순회(preorder) : VLR
-
후위 순회(postorder) : LRV
- Binary tree with arithmetic expression
Inorder traversal
void inorder(treePointer ptr)
{
if(ptr){
inorder(ptr->leftChild);
printf("%d\n", ptr->data);
inorder(ptr->rightChild);
}
}
Preorder traversal
void preorder(treePointer ptr)
{
if(ptr){
printf("%d\n", ptr->data);
preorder(ptr->leftChild);
preorder(ptr->rightChild);
}
}
Postorder traversal
void postorder(treePointer ptr)
{
if(ptr){
postorder(ptr->leftChild);
postorder(ptr->rightChild);
printf("%d\n", ptr->data);
}
}
Level-order traversal
- 각 레벨별로 트리를 순회한다.
- queue를 사용해 각 노드를 push해준다.
void levelorder(treePointer ptr)
{
if(!ptr) return;
push(ptr);
while(!isEmpty())
{
ptr = pop();
if(ptr)
{
printf("%d\n", ptr->data);
if(ptr->leftChild)
push(ptr->leftChild);
if(ptr->rightChild)
push(ptr->rightChild);
}
}
}
Leave a comment